The modern business world is currently in the middle of a gold rush. Everyone is talking about Artificial Intelligence, or AI. It seems like every day a new tool comes out that promises to do our work for us, write our emails, or predict the future. Business owners are rushing to buy these tools because they do not want to be left behind. But there is a big problem that most people are ignoring. They are trying to build a skyscraper on a foundation of sand.
You cannot just buy an AI program, turn it on, and expect magic to happen. AI is like a very high performance sports car. It has an incredible engine and can go very fast. But a car needs fuel to run. If you put water or dirt into the gas tank of a Ferrari, it will not drive. It will break down. In the world of business, data is that fuel. The question is where do you get the fuel.
This is where a data strategy becomes the most important thing you can build.
Many people think a data strategy is just about buying hard drives to store files or making sure your customer list is in an Excel sheet. That is not enough anymore. A true data strategy for AI is a complete plan. It is a roadmap that tells you exactly how you will find data, how you will clean it, how you will protect it, and how you will use it to teach your AI tools.
Without a clear data strategy, your expensive AI tools will fail. They will give you wrong answers. They might even get your company in trouble with the law. This article is going to explain exactly what a data strategy for AI is, why you need one right now, and the specific steps you must take to build one that works.
The Core Components of an AI-Ready Data Strategy
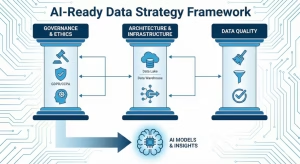
To understand how to build a data strategy, you have to understand the parts that make it work. You cannot just pile all your information into a folder and hope for the best. You need a system. A strong data strategy is built on three main pillars: Governance, Architecture, and Quality.
Data Governance and Ethics
Data governance sounds like a boring legal term, but it is actually the rules of the road. Imagine a city with no stop signs, no speed limits, and no police. Cars would crash everywhere. Governance provides the rules for your data.
A good data strategy includes strict governance. This means you decide who is allowed to see certain data. You decide who can change the data. You also have to follow the law. There are strict laws today like GDPR in Europe or CCPA in California. These laws say you have to be very careful with personal information. If your AI accidentally uses private customer data because you did not have good rules, you could get fined a lot of money.
Also, we have to talk about ethics. AI learns from the data you give it. If you give it data that is unfair or biased, the AI will make unfair decisions. For example, if you only show an AI resumes from men, it might learn to reject resumes from women. A strong data strategy includes humans checking the data to make sure it is fair and honest. This is often called having a “Human in the Loop.”
Data Architecture and Infrastructure
The second pillar of your data strategy is architecture. This is the blueprint of your house. It is the technology you use to hold and move your data.
In the past, businesses used things called Data Warehouses. These were great for structured data. Structured data is information that fits essentially into rows and columns, like a spreadsheet. Phone numbers, zip codes, and prices are structured data.
But today, we have a lot of unstructured data. This includes emails, photos, videos, and social media posts. AI is very good at reading this kind of messy data, but you need a place to put it. This is why modern architecture uses things like Data Lakes. A Data Lake can hold any kind of data until you are ready to use it.
Your data strategy must decide where your data lives. Will you keep it on your own computers in your office? Or will you put it in the cloud using services like Amazon or Microsoft? A good data strategy usually uses the cloud because it is easier to scale up as your business grows.
Data Quality: The “Garbage In, Garbage Out” Principle
The third and perhaps most important pillar is quality. There is a famous saying in computer science: “Garbage In, Garbage Out.” This means if you feed your computer bad information, it will give you bad results.
Imagine you are a restaurant owner. You want to use AI to predict how much food to order for next week. You have a list of all your sales from the last year. But, the list is messy. Some days are missing. Sometimes a waiter typed “$100” instead of “$10.00.” Sometimes the date is wrong.
If you feed that messy list to an AI, it will tell you to order the wrong amount of food. You will lose money.
A robust data strategy includes a cleaning process. You need to fix errors. You need to remove duplicate entries. You need to make sure all the formats are the same. This process is called data normalization. You cannot skip this step. If your data strategy ignores quality, your AI project is doomed to fail before it even starts.
Why Your Business Needs a Specific Strategy for AI
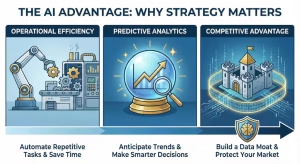
You might be thinking, “Hermes, this sounds like a lot of work. Can I just skip it?” The answer is no. The businesses that win in the next ten years will be the ones that treat their data like gold. Those who ignore their data strategy will struggle to survive. Here is why you need to take this seriously.
Operational Efficiency
Every business has tasks that are boring and repetitive. Maybe your employees spend hours copying numbers from one email to another. Maybe they spend all day scheduling appointments.
AI can do these tasks for you, but only if it knows how. A data strategy helps you organize your information so the AI can read it. When you automate these boring tasks, your employees can spend their time doing more important things, like talking to customers or inventing new products. This makes your whole company run smoother and cheaper.
Predictive Analytics
This is the “crystal ball” part of business. Most companies look at the past. They ask, “What happened last month?” This is useful, but it is not enough.
With a smart data strategy, you can move from looking at the past to predicting the future. This is called predictive analytics. Instead of asking what happened, you ask, “What will happen next month?”
For example, a shoe store with a good data strategy can look at weather patterns, local events, and past sales to guess exactly which boots will sell next November. They can order the right stock before anyone else. This gives them a huge advantage. You cannot do this if your data is messy or lost in a filing cabinet.
Competitive Advantage
Think about your business rivals. They are probably trying to figure out AI too. If you build a solid data strategy now, you are building a wall around your business that protects you. We call this a “moat.”
Your data is unique. Nobody else has your customer list. Nobody else has your sales history. If you organize this data and use it to train an AI, you will have a tool that nobody else in the world has. Your competitors can buy the same software as you, but they cannot buy your data. Your data strategy turns your unique history into a secret weapon.
How to Build a Data Strategy for AI: A 5-Step Roadmap
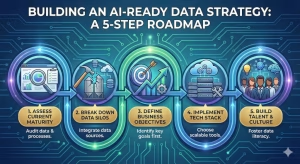
Now that you know what a data strategy is and why you need it, we need to talk about how to build it. You do not have to do everything at once. You can follow these five steps to get started.
Step 1: Assess Current Data Maturity
The first step in any journey is knowing where you are starting. You need to look at your business honestly. How do you handle information right now?
Are you “Data Aware”? This means you know data is important, but you mostly use spreadsheets and manual reports. Or are you “Data Driven”? This means you have a central system and you use numbers to make every big decision.
Most small businesses are just Data Aware. That is okay. Your data strategy starts with an audit. Look at all the software you use. Look at where your files are stored. Ask your team how much time they spend looking for information. This audit will show you the holes in your current process.
Step 2: Break Down Data Silos
Imagine a football team where the offense and the defense never talk to each other. They would lose every game. In many businesses, data is stuck in “silos.”
A silo happens when one department has information that nobody else can see. The sales team has a list of customers. The marketing team has a list of email subscribers. The accounting team has a list of who paid. But these lists are all separate.
A key part of your data strategy is breaking down these silos. You need to connect these systems. When the sales team lands a new client, the marketing team should know immediately. When you integrate your data, your AI can see the whole picture. If the AI can only see half the field, it cannot help you win the game.
Step 3: Define Business Objectives First
This is where many smart people make a mistake. They start with the technology. They say, “I want to use AI.” That is backwards.
Your data strategy should start with a business problem. What are you trying to fix? Do you want to stop customers from leaving? Do you want to sell more products? Do you want to speed up shipping?
Define the goal first. Once you have a goal, you can figure out what data you need to solve it. If your goal is to stop customers from leaving, you need data on customer complaints and returns. If your goal is to sell more, you need data on what products are popular. Let the business need drive the data strategy, not the other way around.
Step 4: Implement the Technology Stack
Once you have a plan, you need the tools. This is your technology stack. There are many options out there, and it can be confusing.
For a small business, you do not need to build a supercomputer. You can use cloud tools that already exist. You might use a database like Snowflake or Databricks to store your information. You might use cloud services from Amazon (AWS) or Microsoft (Azure).
Your data strategy should help you choose tools that fit your budget and your skills. Do not buy a Ferrari if you only know how to drive a go-kart. Start with tools that are easy to use and scale up later. The most important thing is that the tools can talk to each other.
Step 5: Talent and Culture
The final step is about people. You can have the best data strategy in the world, but if your employees do not understand it, it is useless.
You need to create a culture where people respect data. This means training your staff. They need to know why it is important to type data into the system correctly. They need to know how to read the reports the AI generates. This is called Data Literacy.
You might also need to hire an expert. In big companies, there is a person called a Chief Data Officer (CDO). In a small business, you might just need a consultant or a tech-savvy manager to take the lead. Whoever it is, someone needs to be in charge of the data strategy to make sure everyone follows the rules.
Common Challenges and Pitfalls
Building a data strategy is not always easy. There are traps you can fall into. As an expert who has seen many businesses try this, I want to warn you about the most common problems.
Data Security Risks
When you bring all your data together in one place, you create a big target for hackers. If you lose a notebook, it is bad. If you lose your entire customer database, it is a disaster.
Your data strategy must focus heavily on security. You need passwords, encryption, and backups. You need to know exactly who has access to what. Never trade security for speed. It is better to be slow and safe than fast and hacked.
Scalability Issues
Sometimes a business runs a pilot project. They take a small amount of data and test an AI tool. It works great! Everyone is happy.
Then, they try to do the same thing with all their data, and everything breaks. The system gets too slow. The costs go up too high. This is a scalability issue.
A good data strategy plans for growth. You have to ask, “Will this work if we have ten times as many customers?” If the answer is no, you need a better plan. You need infrastructure that can grow with you.
Lack of Stakeholder Buy-in
This is a fancy way of saying that your boss or your employees don’t care. Sometimes, people resist change. They have done things the same way for twenty years and they do not want to learn a new system.
If you create a data strategy in a dark room and then force it on everyone, they will hate it. You need to get people excited. Show them how the data strategy will make their jobs easier. Show them how it will help the business make money. You need everyone on the same team for this to work.
Commonly Asked Questions about Data Strategy
I often get asked specific questions about data strategy by clients at WebHeads United. Here are some of the most common ones.
What is the difference between data strategy and AI strategy?
This is a great question. Think of it like cooking. Data strategy is how you buy the groceries, wash the vegetables, and organize your pantry. It is about the ingredients. AI strategy is the recipe. It is how you cook those ingredients to make a meal. You cannot cook a great meal (AI strategy) if you have rotten ingredients (data strategy). They are different, but you need both.
Key components of an AI data strategy?
As we discussed, the key components are governance (the rules), architecture (the storage), quality (cleanliness), and security (protection). You also need to think about talent (the people). If you miss any one of these, your data strategy will be weak.
How do I start an AI strategy?
The best way to start is small. Do not try to change your whole company in one day. Pick one small problem. Maybe you want to automate your email responses.
Build a mini data strategy just for that one problem. Gather the emails, clean them, and train a simple AI model. When you see it working, you will learn a lot. Then you can try a bigger project. Success builds confidence.
Conclusion
We have covered a lot of ground today. We learned that AI is not magic; it is math. And that math relies entirely on the information you feed it. That is why a data strategy is not just an option anymore; it is a requirement for survival.
A data strategy gives you the power to organize your business. It allows you to follow the law and be ethical. It lets you predict the future instead of just reacting to the past. It turns your unique history into a competitive advantage that no one can steal.
But remember, a data strategy is not a document you write once and put in a drawer. It is a living thing. Your business changes, the technology changes, and the world changes. Your strategy has to change with it. You need to keep checking your data quality. You need to keep training your team.
If you are feeling overwhelmed, that is normal. This is complex stuff. But the fact that you are reading this means you are already ahead of the competition. Most people are just blindly buying tools. You are thinking about the foundation.
Start today. Look at your data. Is it clean? Is it organized? Is it safe? If the answer is no, do not panic. Just start with step one. Assess where you are. Build your plan. Create your data strategy. The future of your business depends on it.